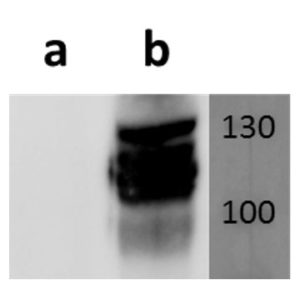
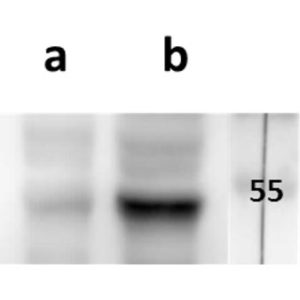
Anti-UL56 (HCMV) antibody
Clone: UL56.07
Catalog No.: HR-HCMV-03
Host Species: Mouse
Reactivity: Human cytomegalovirus
Antigen/Immunogen: The immunogen consisted of UL56 C terminal domain and was produced in E.coli
Tested Applications: ELISA, IF, IP, WB (1:3000)
€200.00 – €1,500.00
Available Options:
Description
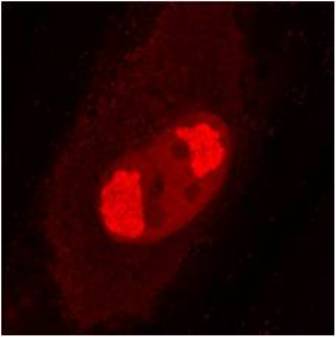
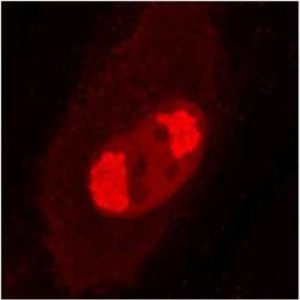
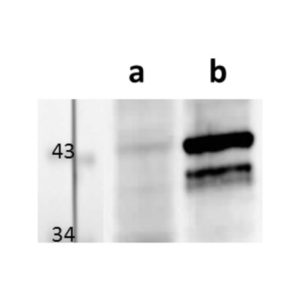
pUL56 is highly conserved 130-kDa DNA binding protein encoded by Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gene UL56. It exists as a dimer formed by association of two ring shaped structures connected to each other by a bridge at their base (FEBS Letters (2004) 563, 135-40). Together with pUL89 it forms HCMV terminase complex. As a large subunit of that complex, pUL56 is required for DNA‐binding and capsid association. Its ATP-ase activity provides energy for the translocation of the concatemers to the preformed capsids (Nucleic Acids Research (2003) 31, 1426-33; Virology (1994) 205, 321-8). Recombinant HCMV interacts with specific HCMV DNA packaging motifs (pac) and is able to cleave DNA bearing these motifs although that function is primary attributed to small terminase subunit pUL89 (Journal of Virology (1998) 72, 2259-64). pUL56 was found to be predominantly localized throughout the nucleus in viral replication centers of infected cells (FEBS Letters (2000) 471, 215-8). Mutations and naturally occurring sequence polymorphisms in UL56 gene have been identified to mediate resistance to benzimidazole derivatives and AIC246 (Letermovir) (Journal of Virology (1998) 72, 4721-8; Antiviral Research (2015) 116, 48-50; Journal of Virology (2011) 85, 10884-93)). pUL56 is a functional homolog of HSV-1 terminase subunit UL28. Our anti-UL56 antibody UL56.07 (described in J. Virol. 2013 Feb;87(3):1720-32), works in ELISA (on immunogen), IF (on HCMV infected cells) and each LOT is validated for Western blot (of HCMV infected cell lysates), where it specifically recognizes a protein species of ~95 kDa, which corresponds well to the predicted size.
Additional information
| FORM | Liquid |
|---|---|
| STORAGE | Long term -20 °C, short term +4 °C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
| CONCENTRATION | 1 mg/mL |
| PURITY | Affinity purified |
| CLONALITY | Monoclonal |
| ISOTYPE | IgG2b |
| LIGHT CHAIN TYPE | kappa |
| REFERENCES | n/a |