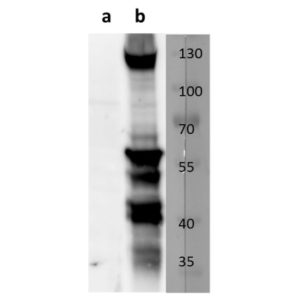
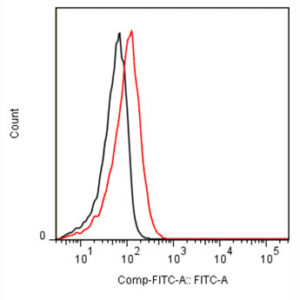
Anti-human NKG2D antibody
Clone: hNKG2D.07
Catalog No.: HR-Lympho-03
Host Species: Mouse
Reactivity: Human
Antigen/Immunogen: The immunogen consisted of NKG2D ectodomain fused to the hIgG1 Fc fragment and was produced from the supernatant of HEK 293T cells
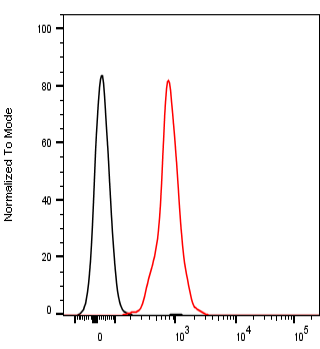
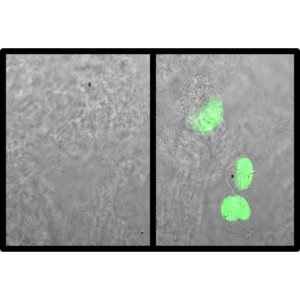
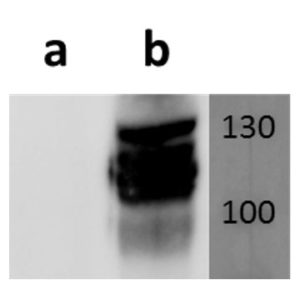
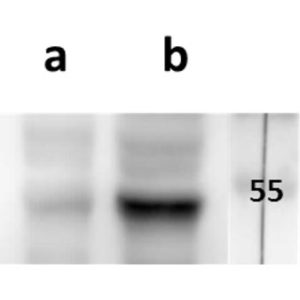
Tested Applications: ELISA, FACS, IF
€200.00 – €1,500.00
Available Options:
Description
Human activating receptor natural-killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) is a 35 kDa type II transmembrane glycoprotein and a part of CD94/NKG2 family of C-type lectin-like receptors (Molfetta et al., 2016, Trends in Immunology, 37(11), 790–802). Encoded by KLRK1 gene, it is expressed by NK cells (acting as an activating receptor but also regulating their differentiation and survival), NKT cells, γδ T cells and CD8+ αβ T cells (providing co-stimulatory signals for T cell activation) (Koehl et al., 2017, Front. Immunol, 8(8)). It forms homodimers, whose lectin-like ectodomains bind various stress-inducible molecules which are mostly absent on the surface of normal cells, but overexpressed by infected, transformed, senescent and stressed cells (Molfetta et al., 2016, Trends in Immunology, 37(11), 790–802). Thus, NKG2D is considered a major recognition receptor implicated in the detection and elimination of transformed and infected cells and its activating signal can overcome the inhibitory signals resulting from MHC class I recognition. Due to short cytoplasmic domain, its signalling requires association with adapter proteins DAP12 (a true activating signal) or DAP10 (resulting in a costimulatory signal), depending on NKG2D isoform (Jelencic et al., 2017 Immunology Letters. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.04.006). Our anti-human NKG2D antibody hNKG2D.07 works in ELISA (on immunogen) and FACS (on human cells).
Additional information
| FORM | Liquid |
|---|---|
| STORAGE | Long term -20 °C, short term +4 °C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. |
| CONCENTRATION | 1 mg/mL |
| PURITY | Affinity purified |
| CLONALITY | Monoclonal |
| ISOTYPE | IgG1 |
| LIGHT CHAIN TYPE | kappa |
| REFERENCES | n/a |